The differential equation d^2y/dx^2 x(dy/dx) siny x^2 = 0 is of the following type`x^y*y^x=1` Find `dy/dx` `x^y*y^x=1` Find `dy/dx` Books Physics NCERT DC Pandey Sunil Batra HC Verma Pradeep Errorless Chemistry If , find and prove that 257 139k LIKES 2786k VIEWS 2786k SHARES FindRead it This problem has been solved!

Exercise Set 3 1 Cas 2 A Find Dy Dx By Chegg Com
X^y.y^x=m find dy/dx
X^y.y^x=m find dy/dx- 1answer If y = sec^1((x 1)/(x 1)) sin^1((x 1)/(x 1)), then write the value of dy/dx askedApr in Differentiationby Kaina(304kpoints) differentiation class12 Welcome to Sarthaks eConnect A unique platform where students can interact with teachers/experts/students to get solutions to their queriesSo we get (1/y)(dy/dx) = log(2) 4) We want to find dy/dx, which is on the LHS To get this dy/dx on its own we can multiply both sides by y So we get dy/dx = y log(2) 5) To finish this question we need to sub in for y and then we have an answer for dy/dx



How To You Find The General Solution Of Dy Dx X Y Socratic
If x^y=y^x ,then find dy/dx Updated On 57 To keep watching this video solution for FREE, Download our App Join the 2 Crores Student community now!Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreTake log on both sides == y log x = log u == y*1/x logx * dy/dx (by products rule) = 1/u du / dx ==du/dx = x y (y/x logx dy/dx) let y x = v ;
How to find dy/dx by implicit differentiation given that e^ (x^2y) = x y Here's the 4 simple steps we will take in order to find dy/dx from the given equation e^ (x^2y) = x y 021Take log on both sides == x log y = logv == x*1/ydy/dx logy*1 (by products rule) = 1/v dv/dx == dv/dx = y x (x/y dy/dx logy) == u v = a b differentiating wrt x we get , du/dx dv/dx = 0 ==`x^y=y^x` then find `(dy)/(dx)` `x^y=y^x` then find `(dy)/(dx)` Doubtnut is better on App Paiye sabhi sawalon ka Video solution sirf photo khinch kar Open App Continue with Mobile Browser Books Physics NCERT DC Pandey Sunil Batra HC Verma Pradeep Errorless Chemistry
If y = sin^1 (x√(1 x) √x √(1 x^2) and dy/dx = 1/2 √x√(1x^2) p, then p is equal toIf sin 2 x 2 cos y xy = 0, then dy/dx = If Slope Of Tangent To Curve Y X 3 At A Point Is Equal To Ordinate Of A Point Then Point Is Leave a Comment Cancel replyFind dy/dx by implicit differentiation xe^y = x y Boost your resume with certification as an expert in up to 15 unique STEM subjects this summer



Differentiation Of Composite Function Let Z F X Y Possesses Continuous Partial Derivatives And Let X G T Y H T Possess Continuous Ppt Download




Rd Sharma Class 12 Maths Solutions Chapter 11 Differentiation
Equalling the red y curve and the blue x curve happens also only in (1,1) and shows that dy/dx = dx/dy = 1 Now for z=z (x,y) Equalling the blue and green functions happens in the red curve x=t, y=t, z=t^t ! Ex 55, 12 Find 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 of the functions in, 𝑥^𝑦 𝑦^𝑥 = 1 𝑥^𝑦 𝑦^𝑥 = 1 Let 𝑢 = 𝑥^𝑦 , 𝑣 = 𝑦^𝑥 Hence, 𝑢𝑣=1 Differentiating both sides 𝑤𝑟𝑡𝑥 (𝑑(𝑣〖 𝑢〗))/𝑑𝑥 = 𝑑(1)/𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑣/𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑢/𝑑𝑥 = 0 (Derivative of answered by Nakul01 (369k points) selected by KumariMuskan Best answer Given, xy = yx Taking logarithm on both sides, we get y log x = x log y Differentiating both sides, wrt x y (1/x) log x (dy/dx) = x (1/y) (dy/dx) log y 1 (y/x) (log x) (dy/dx) = (x/y) (dy/dx) log y



Use Fourth Order Runge Kutta Method To Find The Value Of Y At X 1 Given That Dy Dx Y X Y X Such That Y 0 1 Taking H 0 5




Find Dy Dx By Implicit Differentiation X Y Y X Dy Dx Homeworklib
find dy/dx x^yy^x=e^xyFind dy/dx y=3^x y = 3x y = 3 x Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (y) = d dx (3x) d d x ( y) = d d x ( 3 x) The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′ y' y ′ Differentiate using the Exponential Rule which states that d dx ax d d x a x is axln(a) a xYx = xyTaking log on both sides⇒ logyx = logxy⇒ xlogy = ylogx⇒ xy1 dxdy logy×1= xy logxdxdy ⇒ (yx −logx) dxdy = xy −logy⇒ dxdy = yx −logxxy −logy = x(x−ylogx)y(y−xlogy) = x(ylogx−x)y(xlogy−y)




X Y Y X 16 Find Dydx Maths Questions




X 2 Y 2 Xy Find Dy Dx Novocom Top
Till infinite Find dy/dx Please give the solutionWrite in the form y=x^y since x^x^x^x is till infinite, we can consider it to be y, then take l Book a Trial With Our Experts ×See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading Show transcribed image text Expert Answer Who are the experts? To ask Unlimited Maths doubts download Doubtnut from https//googl/9WZjCW If `x^y=y^x`,then find` dy/dx`




For Sin Xy X 0 Using Implicit Differentiation Chegg Com




If X Y Y X Find Dy Dx
Get an answer for 'If x y = xy, then dy/dx = Please explain step by step' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotesFind dy/dx xe^y=xy xey = x − y x e y = x y Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (xey) = d dx (x−y) d d x ( x e y) = d d x ( x y) Differentiate the If x^y y^x = a^b, find dy/dx Sarthaks eConnect Largest Online Education Community




If Y E X Sin 2 X Sin X X Find Dy Dx With Video Teachoo



View Question Y X 3 Then X Y 1 3
Question Find dy/dx by implicit differentiation x sin(y) y sin(x) = 2 x cos(y) sin(x) y' x sin(y) y cos(x) Need Help?Find dy/dx given x^3 3 x^2 y 2 x y^2 = 12 WolframAlpha Have a question about using WolframAlpha? Question Solve dy/dx y/x =xe^x This problem has been solved!




Answered Find Dy Dx For Each Of The Following Bartleby




Answered 3 7 Find The Second Partial Bartleby
Find dy/dx y=e^x y = ex y = e x Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (y) = d dx (ex) d d x ( y) = d d x ( e x) The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′ y' y ′ Differentiate using the Exponential Rule which states that d dx ax d d x a x is axln(a) a x ln ( a) where a a = e e ex e x Davneet Singh is a graduate from Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur He has been teaching from the past 10 years He provides courses for Maths and Science at TeachooThe functions apart and



4 2 Implicit Differentiation




X To The Power Y Y To The Power X A To The Power B Then Find Dy Dx Brainly In
x y y x = a b, here ab is const let x y = u ;Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ If y = x^x , then find dydx Join / Login > 12th > Maths > Continuity and Differentiability > Logarithmic DifferentiationWatch Video in App This browser does not support the video element 5453 k 1714 k Answer



Ii Use The Inverse Rule To Find Dy Dx 1 X Y Y2 Gauthmath



Find Dy Dx When X And Y Are Connected By The Relation X2 Y2 2 Xy Studyrankersonline
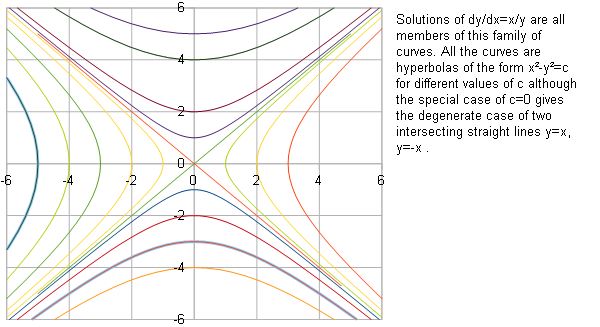
Find dy/dx of y = a^x To differentiate a function of the form y=a^x you need to use a neat little trick to rewrite a^x in the form of something you already know how to differentiate Using the fact that e^ln(x) is equal to x, y = a^x can be written as e^(ln(a)^x) Using log rules ln(a)^x can be written as xlna so now y can now be expressed as yFind `dy/dx` of function x y y x = 1 Advertisement Remove all ads Explanation dy dx = x y ydy = xdx by exploiting the notation (separation) ∫ydy = ∫xdx further exploiting the notation 1 2 y2 = 1 2x2 d y2 = x2 2d x2 −y2 = − 2d x2 −y2 = c where c = −2d Depending on whether c is positive, negative or zero you get a hyperbola open to the x axis, open to the y =axis, or a pair of straight lines through the




If X Y Y X Then Find Dydx




Ifx Y Y X Log A Find Dy Dx Mathematics Topperlearning Com D6ur8arr
If y = (log x)x xlog x, find "dy"/"dx" Mathematics Advertisement Remove all ads Advertisement Remove all ads Advertisement Remove all ads Sum If y = (log x) x x log x, find `"dy"/"dx"` Advertisement Remove all ads Solution Show Solution Let y =(log x) x x log x Also, let u =(log x) x and v = x log xExperts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high Ex 56, 6 If x and y are connected parametrically by the equations without eliminating the parameter, Find 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥, 𝑥 = 𝑎 (𝜃 – sin𝜃), 𝑦 = 𝑎 (1 cos𝜃)Here 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = (𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝜃)/ (𝑑𝑥/𝑑𝜃) Calculating 𝒅𝒚/𝒅𝜽 𝑦 = 𝑎 (1cos𝜃) 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝜃 = 𝑑 (𝑎 (1




Find Dy Dx When Xy Yx C Maths Continuity And Differentiability Meritnation Com



Find Dy Dx If Y X 2 2x 3 16 2x 5 13 Y Chegg Com
Doing the same, we get that #y^x(lny x/y(dy/dx))# Thus the derivative of the entire function is given by #x^ylnx(dy/dx) x^y(y/x) y^xln y y^x x/y(dy/dx) = 0#Calculus (8th Edition) Edit edition Solutions for Chapter 35 Problem 10E Find dy/dx by implicit differentiationxey = x – y Solutions for problems in chapter 35 1E Ex 56, 4 If x and y are connected parametrically by the equations without eliminating the parameter, Find 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥, 𝑥 = 4𝑡, 𝑦 = 4/𝑡Here 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = (𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑡)/ (𝑑𝑥/𝑑𝑡) Calculating 𝒅𝒚/𝒅𝒕 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑡 " " = 𝑑/𝑑𝑡 (4/𝑡) 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑡 = 4 𝑑/𝑑𝑡 (1/𝑡) 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑡 = − 𝟒/𝒕^𝟐 Calculating 𝒅𝒙/𝒅𝒕 𝑑𝑥/𝑑𝑡 = 𝑑 (4𝑡)/𝑑𝑡 𝑑𝑥/𝑑𝑡 " " =




If X2 Y2 2 Xy Find Dy Dx Mention Each And Every Step Mathematics Topperlearning Com Gwvwfskk




If X Y Y X 1 Prove That Dy Dx Y Y Xlogy X Ylogx X
Example 25 Find 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 , if y sin y = cos𝑥 y sin y = cos x Differentiating both sides by x 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 (𝑑(sin〖𝑦)〗)/𝑑𝑥 = (𝒅(𝐜𝐨𝐬〖𝒙)〗)/𝒅𝒙 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 (𝑑(〖sin 〗〖𝑦)〗)/𝑑𝑥 = − sin x 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 (𝒅(𝐬𝐢𝐧〖𝒚)〗)/𝒅𝒚 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥 = − sin x 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading Show transcribed image text Expert Answer Who are the experts?Calculus Find dy/dx y=xe^x y = xex y = x e x Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (y) = d dx (xex) d d x ( y) = d d x ( x e x) The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′ y' y ′ Differentiate the right side of the equation Tap for more steps



If Cosx Y Siny X Find Dy Dx Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




If Y X 1 X Show That 2x Dydx Y 2 X
Mulitply both sides by $dx$ $$d(x^y)=yx^{y1}dxx^y\ln(x)dy, \qquad d(y^x)=y^x\ln(y)dx xy^{x1}dy$$ As you can see, the derivative is of $x^y$ and $y^x$ is the derivative with respect to $x$ on the left side $$ the derivative with repsect to $y$ on the right side




Find Dy Dx If Xy Yx Xx Maths Continuity And Differentiability Meritnation Com



Find Dy Dx When X And Y Are Connected By The Relation Sec X Y Xy Studyrankersonline



Answered Find Dy Dx In Exercises 45 56 Dt X Bartleby




If Y X X Find Dy Dx At X E




Find Dy Dx If Y X 1 X 2




X X 1 Dy Dx X 2 Y X 3 2x 1 Novocom Top




Find Dy Dx Of Function Cos X Y Cos Y X Mathematics Shaalaa Com




If X Y Y X Then Find Dy Dx Youtube




If Xyyx Ab Find Dy Dx Maths Continuity And Differentiability Meritnation Com




Ex 5 3 5 Find Dy Dx In X2 Xy Y2 100 Class 12




For Each Of The Following Find Dy Dx Y X 3 E X Chegg Com
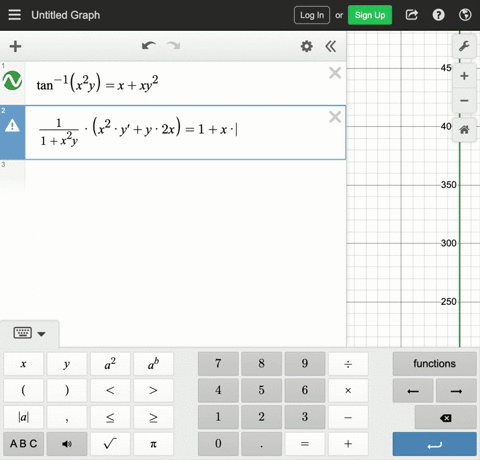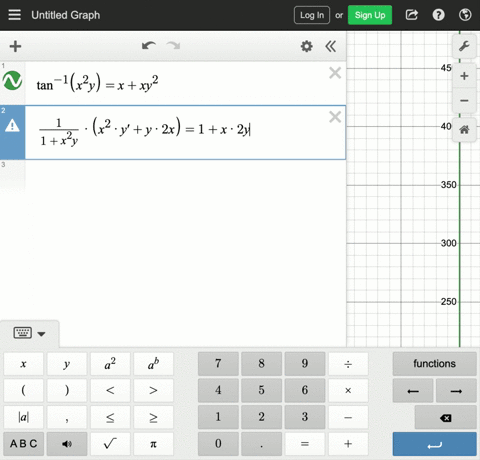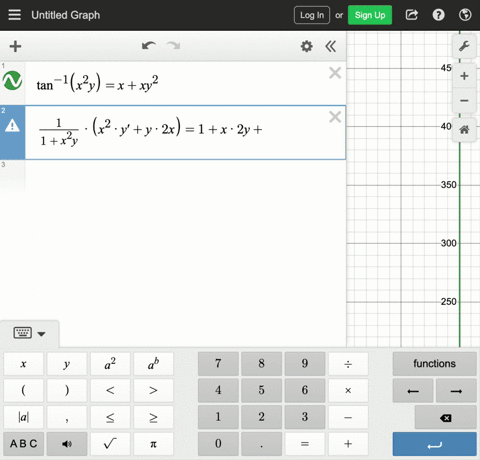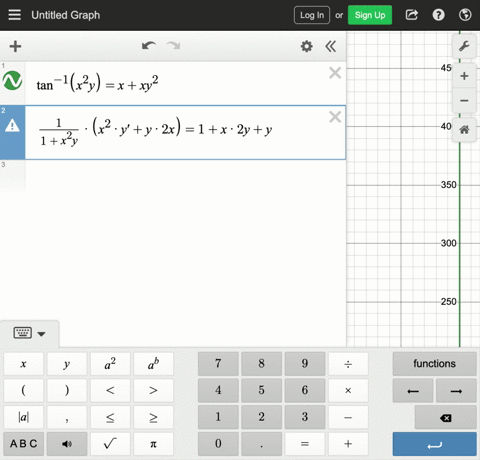



Solved Find Dy Dx By Implicit Differentiation Xy




Dy Dx X Y 1 X Y 3 Novocom Top




If Sin X Y Y X X 2 Y 2 Find Dy Dx




Exercise Set 3 1 Cas 2 A Find Dy Dx By Chegg Com



If X Y Y X What Is Dy Dx Quora



Q Tbn And9gct76rwtg Vjx 0rpyfp1redrp2l5j5euljgxxay9f5hihtsuffx Usqp Cau




Find Dy Dx Of Xy 3 Yx 3 X Mathematics Topperlearning Com D0amnv66



Q Tbn And9gcqfrqxr507ozco1lhgiqwot Cdchophjbocrnsjhblpnw2oyhom Usqp Cau




How To You Find The General Solution Of Dy Dx X Y Socratic




If Y Xcot X 2x2 3 X2 X 2 Find Dy Dx Mention Each And Every Step Mathematics Topperlearning Com Palrsebb




Find Dy Dx If Y E X Sin X Youtube




If Sin Xy X Y X 2 Y Find Dy Dx Brainly In



Jntua Ac In Gate Online Classes Registration Downloads Material A Pdf




Find Dy Dx Of Function Yx Xy Mathematics Shaalaa Com




Find Dy Dx Y X X 1 X Brainly In




Ex 5 5 15 Find Dy Dx Of Xy E X Y Class 12 Ex 5 5



Find Dy Dx When X And Y Are Connected By The Relation Sin Xy X Y X2 Y Studyrankersonline




6 If X Cos Y X3 Tan 1 Y Find Dydx




Find Dy Dx If Xy Yx Log A Maths Continuity And Differentiability Meritnation Com




Find Dy Dx Of Function Xy Yx 1 Mathematics Shaalaa Com




Find Dy Dx If Y X 2 1 X 2 1 Brainly In



1




If Y X X Find Dy Dx For X 0




Find Dy Dx If Y X Cot 1 X Y Brainly In




A Find Dy Dx Of The Following Function Y X Squar Gauthmath




Question 1 Find Dy Dx A Y X 3x Ver B Chegg Com




Derivative Of X Y Y X Calculus 2 Ap Calculus Youtube




Ex 5 3 4 Find Dy Dx In Xy Y2 Tan X Y Chapter 5




Ex 5 3 5 Find Dy Dx In X2 Xy Y2 100 Class 12
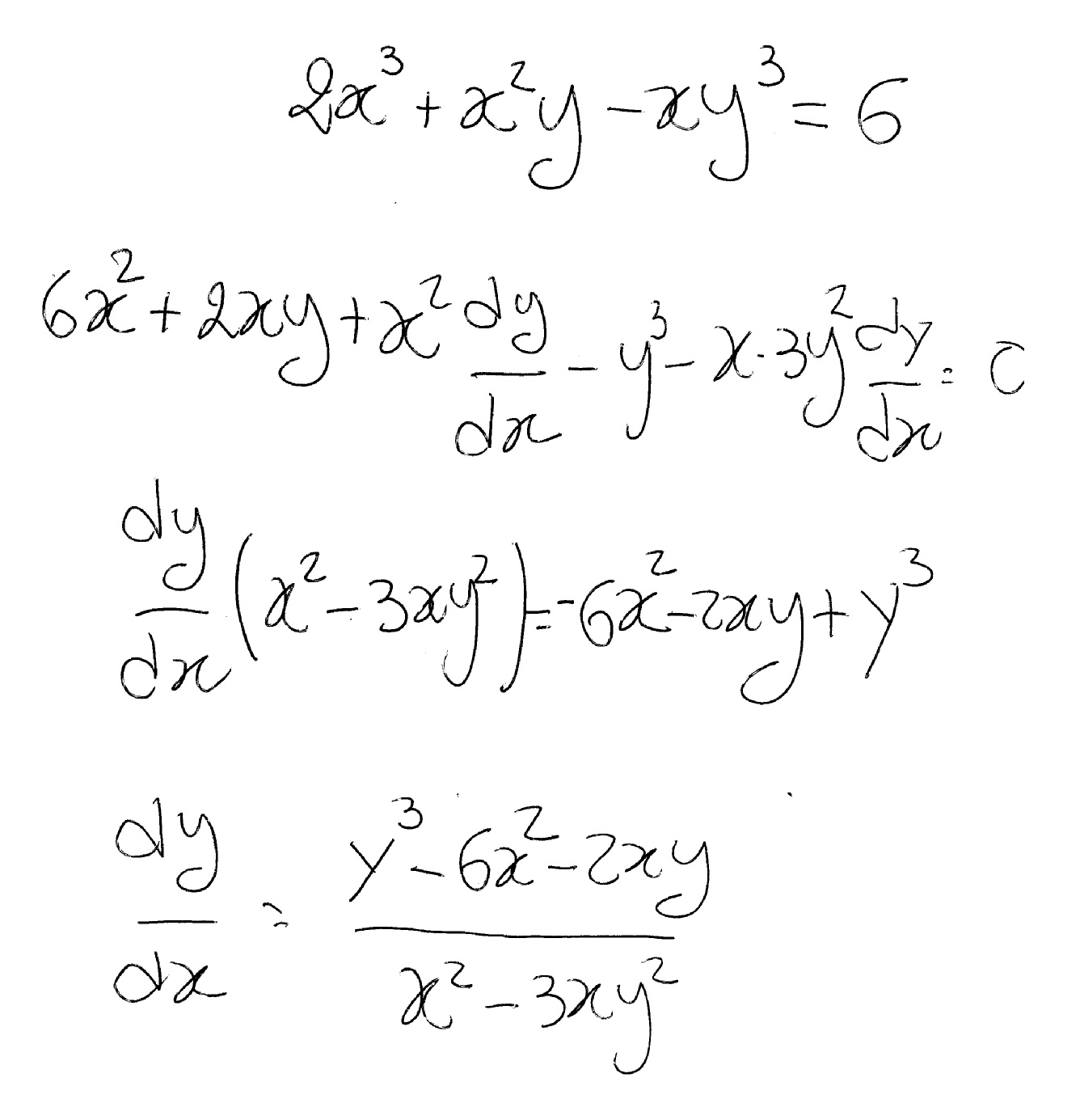



How Do You Find Dy Dx By Implicit Differentiation For 2x 3 X 2 Y Xy 3 6 Socratic




Given The Equation Y Ln X X Ln Y 100 Find Dy Dx Gauthmath




If X Y Y X 2 Find Dy Dx




Find A Derivative With Step By Step Math Problem Solver



Find Dy Dx If Y X X Y A B Where A B Are Constants Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Find Dy Dx If X Y Y X A B Maths Limits And Derivatives Meritnation Com




If Y X 1 X Find Dy Dx Youtube



If X Y Y X What Is Dy Dx Quora



4 2 Implicit Differentiation




Find Dy Dx Of Y X X Siny Scholr




Ex 5 5 14 Find Dy Dx Of Cos X Y Cos Y X Chapter 5 Class 12




Y 2 Xy Tan X Y Then Find Dy Dx Youtube



1




If Y X What Is Dy Dx Quora



What Is The Derivative Of X Y Y X 11 Quora



If Xy Tan X Y Then Find Dy Dx Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
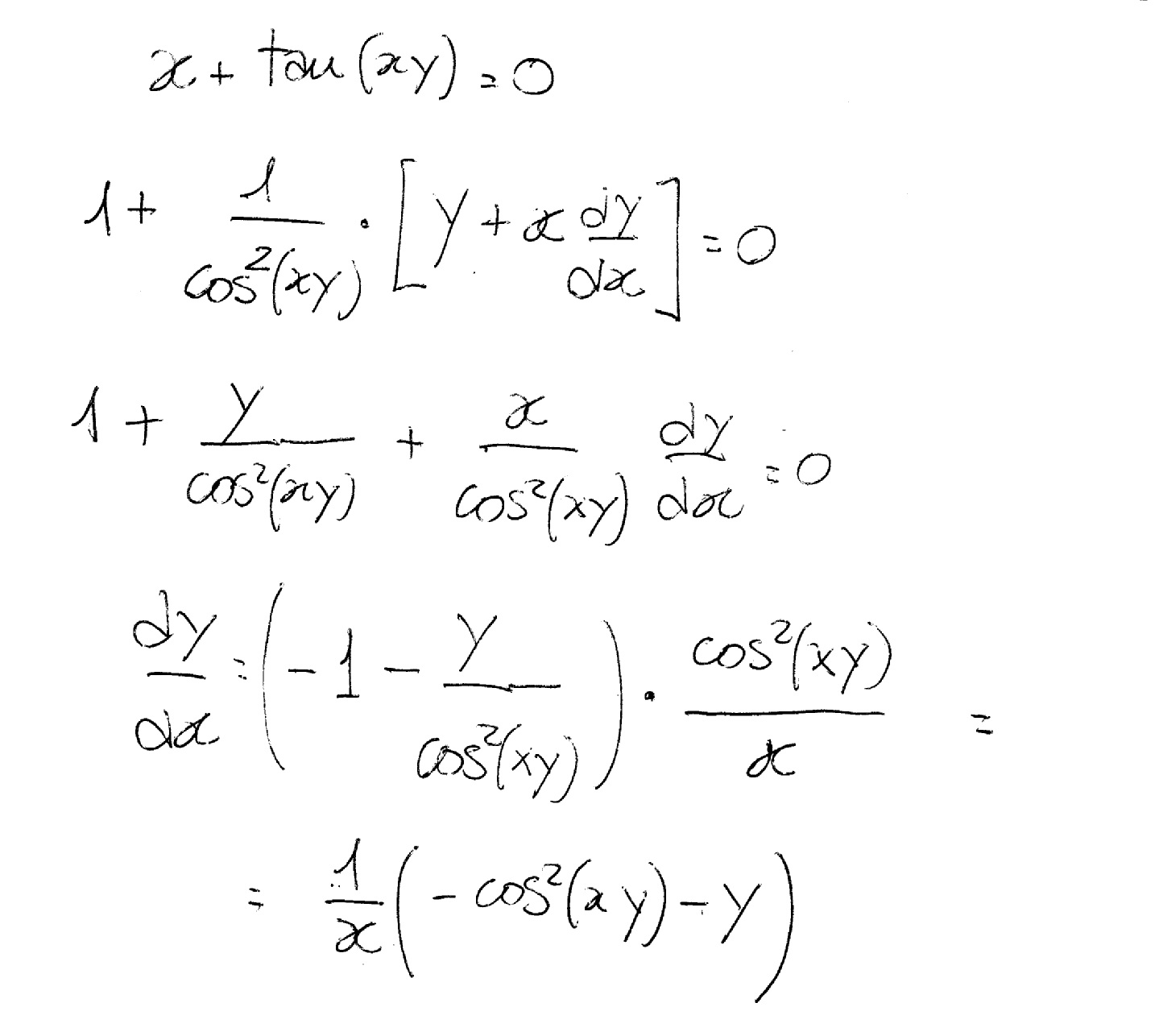



How Do You Find Dy Dx If X Tan Xy 0 Socratic




Find Dy Dxof Y X Logx Log X X Homeworklib




Given That Dy Dx Log10 X Y Y 0 1 Find Y 0 2 Using Modified Euler S Method Mathematics 3 Question Answer Collection




5 Find Dy Dx By Implicit Differentiation 5 X Chegg Com




Ordinary Differential Equations Methods Of Numerical Analysis Assignment Docsity




X Tan Y X Y Dx Xdy 0 Novocom Top




Ex 5 5 12 Find Dy Dx Xy Yx 1 Class 12 Cbse Ncert




Example 33 Find Dy Dx If Y X X Y X X A B Teachoo




How Do You Find Dy Dx For Y 2x Sqrt X 1 Socratic



Write The Formula For Runge Kutta Fourth Order Method




Ex 5 5 15 Find Dy Dx Of Xy E X Y Class 12 Ex 5 5



Find Dy Dx When X And Y Are Connected By The Relation If X Ex Y Prove That Dy Dx X Y X Log X Studyrankersonline
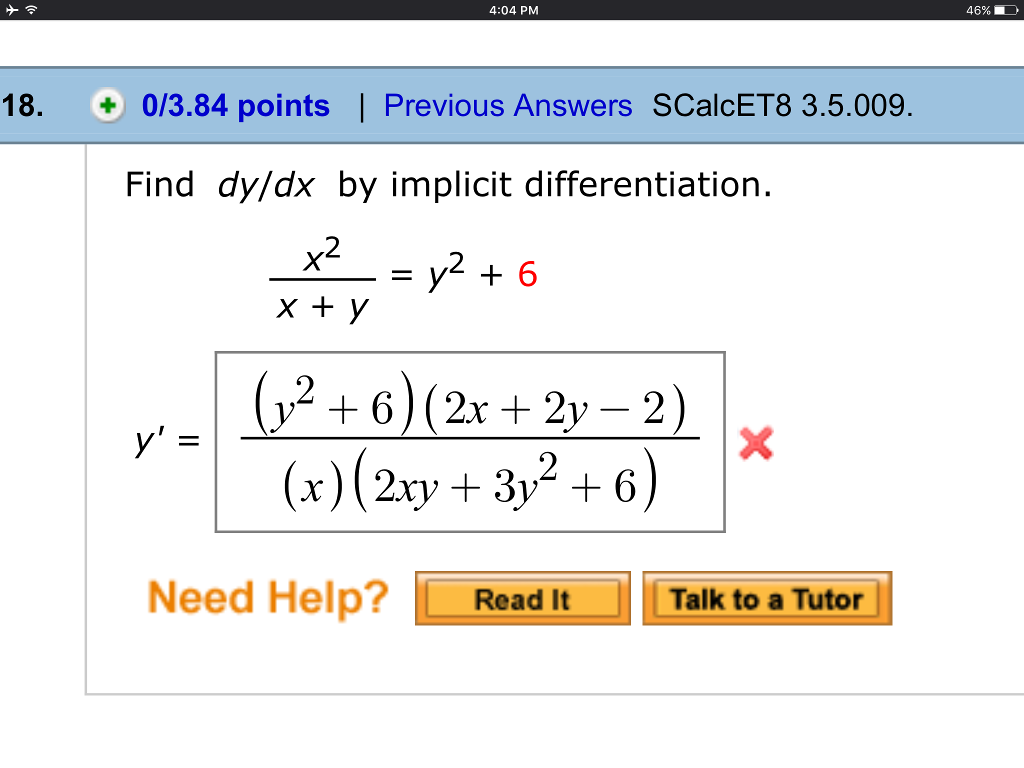



Find Dy Dx By Implicit Differentiation X 2 X Y Chegg Com




If Y X X Prove That D 2y Dx 2 1 Y Dy Dx 2 Y X 0 Brainly In




Find Dy Dx If X Y Xy 3 Maths Application Of Derivatives Meritnation Com




If Xx Xy Yx Ab Then Find Dy Dx Mathematics Shaalaa Com



Www Math Colostate Edu Clayton Teaching M113f10 Homework Hw7solutions Pdf




Pin On Math Videos




D Y D X Y Zonealarm Results




4 Using The Product Rule Find Dy Dx For The Function Y X 2 2x 2 3 5 Using The Chain Rule Find Dy Dx For The Function Y 2x 3 X 2 6x 1 3 6 Find D 2 Dx 2 For The Function Y Sin X Cos X 7



If X Y Y X A B Find Dy Dx Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Find Dy Dx Of Function Xy E X Y Mathematics Shaalaa Com



If X Y Y X What Is Dy Dx Quora



If Y X 3 E X Sin X Then Find Dy Dx Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿